


Next: About this document ...
Up: description
Previous: C. Resolution and dycore-dependent
Contents
- 1
- Alcamo, J., A. Bouwman, J. Edmonds, A. Grubler, T. Morita, and A. Sugandhy, An
evaluation of the ipcc is92 emission scenarios, in Climate Change 1994:
Radiative Forcing of Climate Change and an Evaluation of the IPCC IS92
Emission Scenarios, edited by J. Houghton, 247-304, Cambridge University
Press, 1995.
- 2
- Ammann, C. M., G. A. Meehl, W. M. Washington, and C. S. Zender, A monthly and
latitudinally varying volcanic forcing dataset in simulations of 20th century
climate, Geophys. Res. Lett., 30 (12),
DOI 1029/2003GL016875, 2003, article no. 1657.
- 3
- Anderson, G. P., S. A. Clough, F. X. Kneizys, J. H. Chetwynd, and E. P.
Shettle, AFGL atmospheric constituent profiles (0-120 km), Technical Report
AFGL-TR-86-0110, AFGL (OPI), Hanscom AFB, MA. 01736, 1986.
- 4
- Anthes, R. A., Summary of workshop on the NCAR Community Climate/forecast
Models 14-26 July 1985, Boulder, Colorado, Bull. Am. Meteorol.
Soc., 67, 94-198, 1986.
- 5
- Arakawa, A., and V. R. Lamb, A potential enstrophy and energy conserving scheme
for the shallow-water equations, Mon. Wea. Rev., 109, 18-36,
1981.
- 6
- Asselin, R., Frequency filter for time integrations, Mon. Wea. Rev., 100, 487-490, 1972.
- 7
- Austin, P., Y. Wang, R. Pincus, and V. Kujala, Precipitation in stratocumulus
clouds: Observational and modeling results, J. Atmos. Sci., 52,
2329-2352, 1995.
- 8
- Baede, A. P. M., M. Jarraud, and U. Cubasch, Adiabatic formulation and
organization of ECMWF's model, Technical Report 15, ECMWF, Reading, U.K.,
1979.
- 9
- Baker, M. B., Variability in concentrations of cloud condensation nuclei in the
marine cloud-topped boundary layer, Tellus, 45B, 458-472, 1993.
- 10
- Balkanski, Y. J., D. J. Jacob, G. M. Gardner, W. C. Graustein, and K. K.
Turekian, Transport and residence times of tropospheric aerosols inferred
from a global three-dimensional simulation of
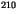 Pb, J. Geophys.
Res., 98, 20,573-20,586, 1993.
Pb, J. Geophys.
Res., 98, 20,573-20,586, 1993.
- 11
- Barth, M. C., D. A. Hegg, and P. V. Hobbs, Numerical modeling of cloud and
precipitation chemistry associated with two rainbands and some comparisons
with observations, J. Geophys. Res., 97, 5825-5845, 1992.
- 12
- Barth, M. C., P. J. Rasch, J. T. Kiehl, C. M. Benkovitz, and S. E. Schwartz,
Sulfur chemistry in the National Center for Atmospheric Research
Community Climate Model: Description, evaluation, features and
sensitivity to aqueous chemistry, J. Geophys. Res., 105,
1387-1415, 2000.
- 13
- Bates, J. R., F. H. M. Semazzi, R. W. Higgins, and S. R. Barros, Integration of
the shallow water equations on the sphere using a vector semi-Lagrangian
scheme with a multigrid solver, Mon. Wea. Rev., 118, 1615-1627,
1990.
- 14
- Bath, L., J. Rosinski, and J. Olson, User's Guide to NCAR CCM2, Technical
Report NCAR/TN-379+IA, National Center for Atmospheric Research, Boulder, CO,
156 pp., 1992.
- 15
- Bath, L. M., M. A. Dias, D. L. Williamson, G. S. Williamson, and R. J. Wolski,
User's Guide to NCAR CCM1, Technical Report NCAR/TN-286+IA, National
Center for Atmospheric Research, Boulder, CO, 173 pp., 1987.
- 16
- Benkovitz, C. M., C. M. Berkowitz, R. C. Easter, S. Nemesure, R. Wagener, and
S. E. Schwartz, Sulfate over the North Atlantic and adjacent continental
regions: Evaluation for October and November 1986 using a
three-dimensional model driven by observation-derived meteorology, jgr,
99, 20,725-20,756, 1994.
- 17
- Berger, A. L., Long-term variations of daily insolation and quaternary climatic
changes, J. Atmos. Sci., 35, 2362-2367, 1978.
- 18
- Betts, A. K., Parametric interpretation of trade-wind cumulus budget studies,
J. Atmos. Sci., 32, 1934-1945, 1975.
- 19
- Bitz, C. M., Documentation of a lagrangian sea ice thickness distribution model
with energy-conserving thermodynamics, Technical report, U. of Washington
APL-UW TM 4-99, 2000.
- 20
- Bitz, C. M., and W. H. Lipscomb, An energy-conserving thermodynamic model of
sea ice, J. Geophys. Res., 104, 15669-15677, 1999.
- 21
- Blanchard, D. C., and A. H. Woodcock, Production, concentration, and vertical
distribution of the sea salt aerosol, Annals New York Acad. Sci., 338, 330-347, 1980.
- 22
- Bonan, G. B., A land surface model (LSM version 1.0) for ecological,
hydrological, and atmospheric studies: Technical description and user's
guide, Technical Report NCAR/TN-417+STR, National Center for Atmospheric
Research, Boulder, CO, 150 pp., 1996.
- 23
- Bonan, G. B., K. W. Oleson, M. Vertenstein, S. Levis, X. Zeng, Y. Dai, R. E.
Dickinson, , and Z.-L. Yang, The land surface climatology of the Community
Land Model coupled to the NCAR Community Climate Model, J. Climate, 15, 3123-3149, 2002.
- 24
- Bourke, W., B. McAvaney, K. Puri, and R. Thurling, Global modeling of
atmospheric flow by spectral methods, in Methods in Computational
Physics, Vol. 17, 267-324, Academic Press, New York, 1977.
- 25
- Boville, B. A., and C. S. Bretherton, Heating and dissipation in the NCAR
community atmosphere model, J. Climate, 16, 3877-3887, 2003.
- 26
- Boville, B. A., J. T. Kiehl, P. J. Rasch, and F. O. Bryan, Improvements to the
ncar csm-1 for transient climate simulations, J. Climate, 14,
164-179, 2001.
- 27
- Briegleb, B. P., Delta-Eddington approximation for solar radiation in the
NCAR Community Climate Model, J. Geophys. Res., 97,
7603-7612, 1992.
- 28
- Briegleb, B. P., C. M. Bitz, E. C. Hunke, W. H. Lipscomb, and J. L. Schramm,
Description of the community climate system model version 2 sea ice model,
Technical report, National Center for Atmospheric Research,
http://www.cesm.ucar.edu/models/ice-csim4, 2002.
- 29
- Bryan, F. O., B. G. Kauffman, W. G. Large, and P. R. Gent, The NCAR CSM
Flux Coupler, Technical Report NCAR/TN-424+STR, National Center for
Atmospheric Research, Boulder, Colorado, 58 pp., 1996.
- 30
- Cess, R. D., Nuclear war: Illustrative effects of atmospheric smoke and dust
upon solar radiation, Clim. Change, 7, 237-251, 1985.
- 31
- Chen, C., and W. R. Cotton, The physics of the marine stratocumulus-capped
mixed layer, J. Atmos. Sci., 44 (50), 2951-2977, 1987.
- 32
- Chervin, R. M., Interannual variability and seasonal climate predictability,
J. Atmos. Sci., 43, 233-251, 1986.
- 33
- Clough, S. A., F. X. Kneizys, and R. W. Davies, Line shape and the water vapor
continuum, Atmos. Res., 23, 229-241, 1989.
- 34
- Clough, S. A., M. J. Iacono, and J. L. Moncet, Line-by-line calculations of
atmospheric fluxes and cooling rates - Application to water vapor, J. Geophys. Res., 97, 15761-15785, 1992.
- 35
- Coakley, J. A., R. D. Cess, and F. B. Yurevich, The effect of tropospheric
aerosols on the Earth's radiation budget: A parameterization for climate
models, J. Atmos. Sci., 40, 116-138, 1983.
- 36
- Colella, P., and P. R. Woodward, The piecewise parabolic method (ppm) for
gas-dynamical simulations, J. Comp. Phys., 54, 174-201, 1984.
- 37
- Collins, W. D., A global signature of enhanced shortwave absorption by clouds,
J. Geophys. Res., 103, 31669-31679, 1998.
- 38
- Collins, W. D., Parameterization of generalized cloud overlap for radiative
calculations in general circulation models, J. Atmos. Sci., 58,
3224-3242, 2001.
- 39
- Collins, W. D., P. J. Rasch, B. E. Eaton, B. Khattatov, J.-F. Lamarque, and
C. S. Zender, Simulating aerosols using a chemical transport model with
assimilation of satellite aerosol retrievals: Methodology for INDOEX,
J. Geophys. Res., 106, 7313-7336, 2001.
- 40
- Collins, W. D., J. K. Hackney, and D. P. Edwards, A new parameterization for
infrared emission and absorption by water vapor in the National Center
for Atmospheric Research Community Atmosphere Model, J. Geophys. Res., 107 (D22), 2002a.
- 41
- Collins, W. D., P. J. Rasch, B. E. Eaton, D. W. Fillmore, J. T. Kiehl, T. C.
Beck, and C. S. Zender, Simulation of aerosol distributions and radiative
forcing for INDOEX: Regional climate impacts, J. Geophys. Res.,
107, DOI 10.1029/2001JD001365, 2002b, article no. 8028.
- 42
- Cooke, W. F., C. Liousse, H. Cachier, and J. Feichter, Construction of a 1
degrees x 1 degrees fossil fuel emission data set for carbonaceous aerosol
and implementation and radiative impact in the ECHAM4 model, J. Geophys. Res., 104, 22137-22162, 1999.
- 43
- Côté, J., and A. Staniforth, A two-time-level semi-Lagrangian
semi-implicit scheme for spectral models, Mon. Wea. Rev., 116,
2003-2012, 1988.
- 44
- Curtis, A. R., Contribution to a discussion of `A statistical model for water
vapour absorption' by R. M. Goody, Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc., 78, 638-640, 1952.
- 45
- Dai, Y., X. Zeng, R. E. Dickinson, and coauthors, The Common Land Model:
Documentation and User's Guide, http://climate.eas.gatech.edu/dai/clmdoc.pdf, 2001.
- 46
- Daley, R., C. Girard, J. Henderson, and I. Simmonds, Short-term forecasting
with a multi-level spectral primitive equation model. Part I--model
formulation, Atmosphere, 14, 98-116, 1976.
- 47
- Dana, T. M., and J. M. Hales, Statistical aspects of the washout of
polydisperse aerosols, Atmos. Environ., 10, 45-50, 1976.
- 48
- Deardorff, J. W., Parameterization of the planetary boundary layer for use in
general circulation models, Mon. Wea. Rev., 100, 93-106, 1972.
- 49
- Demore, W. B., S. P. Sander, C. J. Howard, A. R. Ravishankara, D. M. Golden,
C. E. Kolb, R. F. Hampson, M. J. Kurylo, and M. J. Molina, Chemical kinetics
and photochemical data for use in stratospheric modeling: Evaluation number
12, Technical Report JPL Publ. 97-4, JPL, 266 pp., 1997.
- 50
- Dickinson, R. E., A. Henderson-Sellers, P. J. Kennedy, and M. F. Wilson,
Biosphere-atmosphere transfer scheme (BATS) for the NCAR Community
Climate Model, Technical Report NCAR/TN-275+STR, National Center for
Atmospheric Research, Boulder, Colorado, 69 pp., 1987.
- 51
- Donner, L., and V. Ramanathan, Methane and nitrous oxide: Their effects on
the terrestrial climate, J. Atmos. Sci., 37, 119-124, 1980.
- 52
- Dütsch, H. U., Vertical ozone distribution on a global scale, Pure
Appl. Geophys., 116, 511-529, 1986.
- 53
- Duynkerke, P. G., Application of the E-
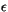 turbulence closure model to
the neutral and stable atmospheric boundary layer, J. Atmos. Sci., 45, 865-880, 1988.
turbulence closure model to
the neutral and stable atmospheric boundary layer, J. Atmos. Sci., 45, 865-880, 1988.
- 54
- Dyer, A. J., A review of flux-profile relationships, Boundary Layer
Meteorol., 7, 363-372, 1974.
- 55
- Ebert, E. E., and J. A. Curry, A parameterization of ice cloud optical
properties for climate models, J. Geophys. Res., 97, 3831-3836,
1992.
- 56
- Ebert, E. E., and J. A. Curry, An intermediate one-dimensional thermodynamic
sea ice model for investigating ice-atmosphere interactions, J. Geophys.
Res., 98, 10085-10109, 1993.
- 57
- Edwards, D. P., GENLN2: A general line-by-line atmospheric transmittance
and radiance model, Technical Report NCAR/TN-367+STR, NCAR, P.O. Box 3000,
Boulder, Colorado, 80307-3000, 147 pp., January, 1992.
- 58
- Feichter, J., E. Kjellström, H. Rodhe, F. Dentener, J. Lelieveld, and G.-J.
Roelofs, Simulation of the tropospheric sulfur cycle in a global climate
model, Atmos. Environ., 30 (10), 1693-1707, 1996.
- 59
- Garcia, R. R., and S. Solomon, A new numerical model of the middle atmosphere.
part ii: Ozone and related species, J. Geophys. Res., 99,
12937-12951, 1994.
- 60
- Geleyn, J.-F., Interpolation of wind, temperature and humidity values from
model levels to the height of measurement, Tellus, Series A (Dynamic
Meteorology and Oceanography), 40A, 347-351, 1988.
- 61
- Godson, W. L., The evaluation of infra-red radiative fluxes due to atmospheric
water vapour, Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc., 79, 367-379, 1953.
- 62
- Goody, R. M., and Y. L. Yung, Atmospheric Radiation. Oxford Univ. Press,
New York, 2nd edition, 1989, 519 pp.
- 63
- Grenfell, T. C., S. G. Warren, and P. C. Mullen, Reflection of solar radiation
by the antarctic snow surface at ultraviolet, visible, and near-infrared
wavelengths, J. Geophys. Res., 99, 18669-18684, 1994.
- 64
- Hack, J. J., Parameterization of moist convection in the National Center
for Atmospheric Research Community Climate Model (CCM2), J. Geophys. Res., 99, 5551-5568, 1994.
- 65
- Hack, J. J., L. M. Bath, G. W. Williamson, and B. A. Boville, Modifications and
enhancements to the NCAR Community Climate Model (CCM1), Technical
Report NCAR/TN-336+STR, National Center for Atmospheric Research, Boulder,
Colorado, 97 pp., 1989.
- 66
- Hack, J. J., B. A. Boville, B. P. Briegleb, J. T. Kiehl, P. J. Rasch, and D. L.
Williamson, Description of the NCAR Community Climate Model
(CCM2), Technical Report NCAR/TN-382+STR, National Center for Atmospheric
Research, 120 pp., 1993.
- 67
- Hansen, J., A. Lacis, D. Rind, G. Russell, P. Stone, I. Fung, R. Ruedy, and
J. Lerner, Climate sensitivity: Analysis of feedback mechanisms, in Climate Processes and Climate Sensitivity, edited by J. E. Hansen, and
T. Takahashi, 130-163, Amer. Geophys. Union, Washington, D.C., 1984.
- 68
- Held, I. M., and M. J. Suarez, A proposal for the intercomparison of the
dynamical cores of atmospheric general circulation models, Bull. Am.
Meteorol. Soc., 75, 1825-1830, 1994.
- 69
- Hess, M., P. Koepke, and I. Schult, Optical properties of aerosols and clouds:
the software package OPAC, Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc., 79,
831-844, 1998.
- 70
- Hesstvedt, E., O. Hov, and I. S. A. Isaksen, Quasi-steady-state approximation
in air pollution modeling: Comparison of two numerical schemes of oxidant
prediction, International Journal of Chemical Kinetics, 10,
971-994, 1978.
- 71
- Hildebrand, F. B., Introduction to Numerical Analysis. McGraw-Hill, New
York, New York, 1956, 511 pp.
- 72
- Hoffmann, M. R., and J. G. Calvert, Chemical transportation modules for
Eulerian acid deposition models, vol. II, The aqueous-phase chemistry,
Rep. EPA/600/3-85/017, Environ. Prot. Agency, Research Triangle Park, N.
C., 1985.
- 73
- Hogstrom, U., Non-dimensional wind and temperature profiles in the atmospheric
surface layer: a re-evaluation, Boundary Layer Meteorol., 42,
55-78, 1988.
- 74
- Holtslag, A. A. M., and B. A. Boville, Local versus nonlocal boundary-layer
diffusion in a global climate model, J. Climate, 6, 1825-1842,
1993.
- 75
- Holtslag, A. A. M., E. I. F. deBruijn, and H.-L. Pan, A high resolution air
mass transformation model for short-range weather forecasting, Mon. Wea.
Rev., 118, 1561-1575, 1990.
- 76
- Holtslag, A. A. M., and C.-H. Moeng, Eddy diffusivity and countergradient
transport in the convective atmospheric boundary layer, J. Atmos. Sci.,
48, 1690-1698, 1991.
- 77
- Hortal, M.
1999.
Aspects of the numerics of the ECMWF model.
in Proceedings of ECMWF Seminar: Recent developments in
numerical methods for atmospheric modelling, 7-11 September 1998,
127-143, .
- 78
- Hsu, Y.-J. G., and A. Arakawa, Numerical modeling of the atmosphere with an
isentropic vertical coordinate, Mon. Wea. Rev., 118, 1933-1959,
1990.
- 79
- IPCC, Climate Change, 1994 : Radiative Forcing of Climate
Change and an Evaluation of the IPCC IS92 emission Scenarios.
Cambridge University Press, 1995, ed., John T. Houghton.
- 80
- Joseph, J. H., W. J. Wiscombe, and J. A. Weinman, The delta-Eddington
approximation for radiative flux transfer, J. Atmos. Sci., 33,
2452-2459, 1976.
- 81
- Kader, B. A., and A. M. Yaglom, Mean fields and fluctuation moments in unstably
stratified turbulent boundary layers, J. Fluid Mech., 212,
637-662, 1990.
- 82
- Kagann, R. H., J. W. Elkins, and R. L. Sams, Absolute band strengths of
halocarbons F-11 and F-12 in the 8- to 16-
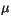 m region, J. Geophys.
Res., 88, 1427-1432, 1983.
m region, J. Geophys.
Res., 88, 1427-1432, 1983.
- 83
- Kalnay, E., M. Kanamitsu, R. Kistler, W. Collins, D. Deaven, L. Gandin,
M. Iredell, S. Saha, G. White, J. Woollen, Y. Zhu, M. Chelliah, W. Ebisuzaki,
W. Higgins, J. Janowiak, K. C. Mo, C. Ropelewski, J. Wang, A. Leetmaa,
R. Reynolds, R. Jenne, and D. Joseph, The NCEP/NCAR 40-year reanalysis
project, Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc., 77, 437-471, 1996.
- 84
- Kasahara, A., Various vertical coordinate systems used for numerical weather
prediction, Mon. Wea. Rev., 102, 509-522, 1974.
- 85
- Kessler, E., On the distribution and continuity of water substance in
atmospheric circulations. Amer. Meteor. Soc., Boston, Mass., 1969.
- 86
- Kettle, A. J., M. O. Andreae, D. Amouroux, and T. W. Andreae, A global database
of sea surface dimethylsulfide (DMS) measurements and a procedure to
predict sea surface DMs as a function of latitude, longitude, and month,
Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles, 13, 399-444, 1999.
- 87
- Kiehl, J. T., and B. P. Briegleb, A new parameterization of the absorptance due
to the 15
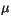 m band system of carbon dioxide, J. Geophys. Res., 96, 9013-9019, 1991.
m band system of carbon dioxide, J. Geophys. Res., 96, 9013-9019, 1991.
- 88
- Kiehl, J. T., and B. P. Briegleb, The relative roles of sulfate aerosols and
greenhouse gases in climate forcing, Science, 260, 311-314,
1993.
- 89
- Kiehl, J. T., J. J. Hack, and B. P. Briegleb, The simulated Earth radiation
budget of the National Center for Atmospheric Research Community
Climate Model CCM2 and comparisons with the Earth Radiation
Budget Experiment (ERBE), J. Geophys. Res., 99,
20815-20827, 1994.
- 90
- Kiehl, J. T., J. Hack, G. Bonan, B. Boville, B. Briegleb, D. Williamson, and
P. Rasch, Description of the NCAR Community Climate Model (CCM3),
Technical Report NCAR/TN-420+STR, National Center for Atmospheric Research,
Boulder, Colorado, 152 pp., 1996.
- 91
- Kiehl, J. T., J. J. Hack, G. B. Bonan, B. B. Boville, D. L. Williamson, and
P. J. Rasch, The National Center for Atmospheric Research Community
Climate Model: CCM3, J. Climate, 11, 1131-1149, 1998.
- 92
- Kiehl, J. T., T. L. Schneider, P. J. Rasch, M. Barth, and J. Wong, Radiative
forcing due to sulfate aerosols from simulations with the National Center
for Atmospheric Research Community Climate Model, Version 3, J. Geophys. Res., , 1441--1457, 2000.
- 93
- Kiehl, J. T., and V. Ramanathan, CO
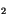 radiative parameterization used in
climate models: comparison with narrow band models and with laboratory data,
J. Geophys. Res., 88, 5191-5202, 1983.
radiative parameterization used in
climate models: comparison with narrow band models and with laboratory data,
J. Geophys. Res., 88, 5191-5202, 1983.
- 94
- Kiehl, J. T., and V. Ramanathan, Comparison of cloud forcing derived from the
Earth Radiation Budget Experiment with that simulated by the NCAR
Community Climate Model, J. Geophys. Res., 95,
11679-11698, 1990.
- 95
- Klein, S. A., and D. L. Hartmann, The seasonal cycle of low stratiform clouds,
J. Climate, 6, 1587-1606, 1993.
- 96
- Kluzek, E. B., M. Vertenstein, and B. E. Eaton, User's Guide to NCAR
CAM2.0, Technical report, National Center for Atmospheric Research, Boulder,
Colorado, http://www.cesm.ucar.edu/models/atm-cam/UsersGuide/cover.html, 2002.
- 97
- Kristjánsson, J. E., and J. Kristiansen, Impact of a new scheme for optical
properties of ice crystals on climates of two gcms, J. Geophys. Res.,
105, 10063-10079, 2000.
- 98
- Lacis, A. A., and V. Oinas, A description of the correlated k distribution
method for modeling nongray gaseous absorption, thermal emission, and
multiple scattering in vertically inhomogeneous atmospheres, J. Geophys.
Res., 96, 9027-9063, 1991.
- 99
- Large, W. G., Ocean modeling and parameterization, in Modeling and
parameterizing the ocean planetary boundary layer, edited by E.P.Chassignet,
and J. (eds.), 81-120, Kluwer Academic Publishers, 1998, Printed in the
Netherlands.
- 100
- Large, W. G., J. C. McWilliams, and S. C. Doney, Oceanic vertical mixing: A
review and a model with a nonlocal boundary layer parameterization, Rev.
Geophys., 32, 363-403, 1994.
- 101
- Large, W. G., and S. Pond, Sensible and latent heat flux measurements over the
ocean, J. Phys. Oceanogr., 12, 464-482, 1982.
- 102
- Lawrence, M. G., and P. J. Crutzen, The impact of cloud particle gravitational
settling on soluble trace gas distributions, Tellus, 50B,
263--289, 1998.
- 103
- Le Texier, H., S. Solomon, and R. R. Garcia, Role of molecular hydrogen and
methane oxidation in the water vapor budget of the stratosphere, Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc., 114, 281-295, 1988.
- 104
- Lean, J., J. Beer, and R. S. Bradley, Reconstruction of solar irradiance since
1610: Implications for climate change, Geophys. Res. Lett., 22,
3195-3198, 1995.
- 105
- Levitus, S., Climatological atlas of the world ocean, Technical Report NOAA
Professional Paper 13, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, 1982.
- 106
- Levkov, L., B. Rockel, H. Kapitza, and E. Raschke, 3D mesoscale numerical
studies of cirrus and stratus clouds by their time and space evolution, Beitr. Phys. Atmosph., 65, 35-58, 1992.
- 107
- Li, J., Accounting for overlap of fractional cloud in infrared radiation, Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc., 126, 3325-3342, 2000.
- 108
- Lin, S.-J., W. C. Chao, Y. C. Sud, and G. K. Walker, A class of the van
leer-type transport schemes and its applications to the moisture transport in
a general circulation model, Mon. Wea. Rev., 122, 1575-1593,
1994.
- 109
- Lin, S.-J., and R. B. Rood, Multidimensional flux form semi-lagrangian
transport schemes, Mon. Wea. Rev., 124, 2046-2070, 1996.
- 110
- Lin, S.-J., and R. B. Rood, An explicit flux-form semi-lagrangian shallow water
model on the sphere, Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc., 123, 2531-2533,
1997.
- 111
- Lin, Y.-L., R. R. Farley, and H. D. Orville, Bulk parameterization of the snow
field in a cloud model, J. Clim. Appl. Meteorol., 22, 1065-1092,
1983.
- 112
- Lind, J. A., and G. L. Kok, Henry's law determination for aqueous solutions of
hydrogen peroxide, methyl hydroperoxide, and peroxyacetic acid, J. Geophys. Res., 91, 7889-7896, 1986.
- 113
- Liousse, C., J. E. Penner, C. Chuang, J. J. Walton, H. Eddleman, and
H. Cachier, A global three-dimensional model study of carbonaceous aerosols,
J. Geophys. Res., 101, 19411-19432, 1996.
- 114
- Locatelli, J. D., and P. V. Hobbs, Fall speeds and masses of solid
precipitation particles, J. Geophys. Res., 79, 2185-2197, 1974.
- 115
- Lohmann, U., and E. Roeckner, Design and performance of a new cloud
microphysics scheme developed for the ECHAM general circulation model, Climate Dynamics, 12, 557-572, 1996.
- 116
- Lord, S. J., W. C. Chao, and A. Arakawa, Interaction of a cumulus cloud
ensemble with the large-scale environment. part iv: The discrete model, J. Atmos. Sci., 39, 104-113, 1982.
- 117
- Maahs, H. G.
1982.
Sulfur dioxide/water equilibrium between 0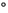 and 50
and 50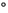 C:
An examination of data at low concentrations.
C:
An examination of data at low concentrations.
in Heterogeneous Atmospheric Chemistry, Geophys. Monogr. Ser.,
volume 26, 273, Washington, D. C. AGU.
- 118
- Machenhauer, B., The spectral method, in Numerical Methods Used in
Atmospheric Models, World Meteorological Organization, Geneva, Switzerland,
1979.
- 119
- Machenhauer, B.
1998.
MPI workshop on conservative transport schemes.
in Report No. 265, . Max-planck-Institute for
Meteorology.
- 120
- Mahowald, N., C. Luo, J. delCorral, and C. Zender, Interannual variability in
atmospheric mineral aerosols from a 22-year model simulation and
observational data, J. Geophys. Res., 2003.
- 121
- Manabe, S., Climate and the ocean circulation: 1. The atmospheric circulation
and the hydrology of the earth's surface, Mon. Wea. Rev., 97,
739-774, 1969.
- 122
- Manabe, S., and F. Möller, On the radiative equilibrium and heat balance of
the atmosphere, Mon. Wea. Rev., 89, 503-562, 1961.
- 123
- Manabe, S., and R. Strickler, Thermal equilibrium of the atmosphere with a
convective adjustment, J. Atmos. Sci., 21, 361-385, 1964.
- 124
- Maykut, G. A., and D. Perovich, The role of shortwave radiation in the summer
decay of a sea ice cover, J. Geophys. Res., 92, 7032-7044, 1987.
- 125
- Maykut, G. A., and N. Untersteiner, Some results from a time-dependent
thermodynamic model of sea ice, J. Geophys. Res., 76, 1550-1575,
1971.
- 126
- McAvaney, B. J., W. Bourke, and K. Puri, A global spectral model for simulation
of the general circulation, J. Atmos. Sci., 35, 1557-1583, 1978.
- 127
- McPhee, M. G., Turbulent heat flux in the upper ocean under sea ice, J. Geophys. Res., 97, 5365-5379, 1992.
- 128
- Moeng, C.-H., and P. P. Sullivan, A comparison of shear- and buoyancy-driven
planetary boundary layer flows, J. Atmos. Sci., 51, 999-1022,
1994.
- 129
- Mote, P. W., J. R. Holton, J. M. Russell, and B. A. Boville, A comparison of
observed (haloe) and modeled (ccm2) methane and stratospheric water vapor,
grl, 20, 1419--1422, 1993.
- 130
- Müller, J.-F., and G. P. Brasseur, IMAGES: A three-dimensional chemical
transport model of the global troposphere, jgr, 100,
16445--16490, 1995.
- 131
- National Bureau of Standards, Selected values of chemical thermodynamic
properties, 1, Tech. Note 270-1, National Bureau of Standards,
Gaithersburg, Md., 1965.
- 132
- Ono, N., Specific heat and heat of fusion of sea ice, in Physics of Snow
and Ice, Vol. I, edited by H. Oura, 599-610, Institute of Low Temperature
Science, Hokkaido, Japan, 1967.
- 133
- Orszag, S. A., Fourier series on spheres, Mon. Wea. Rev., 106,
405-412, 1974.
- 134
- Paulson, C. A., and J. J. Simpson, Irradiance measurements in the upper ocean,
J. Phys. Oceanogr, 7, 952-956.
- 135
- Raisanen, P., Effective longwave cloud fraction and maximum-random overlap of
clouds: A problem and a solution, Mon. Wea. Rev., 126,
3336-3340, 1998.
- 136
- Ramanathan, V., Radiative transfer within the Earth's troposphere and
stratosphere: A simplified radiative-convective model, J. Atmos.
Sci., 33, 1330-1346, 1976.
- 137
- Ramanathan, V., and R. E. Dickinson, The role of stratospheric ozone in the
zonal and seasonal radiative energy balance of the Earth-troposphere
system, J. Atmos. Sci., 36, 1084-1104, 1979.
- 138
- Ramanathan, V., and P. Downey, A nonisothermal emissivity and absorptivity
formulation for water vapor, J. Geophys. Res., 91, 8649-8666,
1986.
- 139
- Ramanathan, V., R. J. Cicerone, H. B. Singh, and J. T. Kiehl, Trace gas trends
and their potential role in climate change, J. Geophys. Res., 90,
5547-5566, 1985.
- 140
- Ramaswamy, V., and S. M. Freidenreich, Solar radiative line-by-line
determination of water vapor absorption and water cloud extinction in
inhomogeneous atmospheres, J. Geophys. Res., 96, 9133-9157,
1991.
- 141
- Rasch, P. J., B. A. Boville, and G. P. Brasseur, A three-dimensional general
circulation model with coupled chemistry for the middle atmosphere, J. Geophys. Res., 100, 9041-9071, 1995.
- 142
- Rasch, P. J., N. M. Mahowald, and B. E. Eaton, Representations of transport,
convection, and the hydrologic cycle in chemical transport models:
Implications for the modeling of short-lived and soluble species, J. Geophys. Res., 102, 28127-28138, 1997.
- 143
- Rasch, P. J., M. C. Barth, J. T. Kiehl, S. E. Schwartz, and C. M. Benkovitz, A
description of the global sulfur cycle and its controlling processes in the
National Center for Atmospheric Research Community Climate
Model, Version 3, J. Geophys. Res., 105, 1367-1385, 2000.
- 144
- Rasch, P. J., and J. E. Kristjánsson, A comparison of the CCM3 model
climate using diagnosed and predicted condensate parameterizations, J. Climate, 11, 1587--1614, 1998.
- 145
- Rasch, P. J., and M. G. Lawrence.
1998.
Recent developments in transport methods at ncar.
in MPI workshop on conservative transport methods, 93 Report No. 265., , Hamburg, Germany. Max Planck Institute for Meteorology.
- 146
- Rasch, P. J., and D. L. Williamson, On shape-preserving interpolation and
semi-Lagrangian transport, SIAM J. Sci. Stat. Comput., 11,
656-687, 1990.
- 147
- Ringler, T. D., R. P. Heikes, , and D. A. Randall, Modeling the atmospheric
general circulation using a spherical geodesic grid: A new class of dynamical
cores, Mon. Wea. Rev., 128, 2471-2490, 2000.
- 148
- Ritchie, H., and M. Tanguay, A comparison of spatially averaged Eulerian and
semi-Lagrangian treatments of mountains, Mon. Wea. Rev., 124,
167-181, 1996.
- 149
- Robert, A. J., The integration of a low order spectral form of the primitive
meteorological equations, J. Meteorol. Soc. Japan, 44, 237-245,
1966.
- 150
- Roberts, R. E., J. E. A. Salby, and L. M. Biberman, Infrared continuum
absorption by atmospheric water vapor in the 8-12
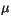 m window, Appl.
Opt., 15, 2085-2090, 1976.
m window, Appl.
Opt., 15, 2085-2090, 1976.
- 151
- Rodgers, C. D., and C. D. Walshaw, The computation of infra-red cooling rate in
planetary atmospheres, Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc., 92, 67-92, 1966.
- 152
- Rothman, L. S., A. Goldman, J. R. Gillis, R. R. Gamache, H. M. Pickett, R. L.
Poynter, N. Husson, and A. Chedin, AFGL trace gas compilation - 1982
version, Appl. Opt., 22, 1616-1627, 1983.
- 153
- Rothman, L. S., A. Barbe, D. C. Benner, L. R. Brown, C. Camy-Peyret, M. R.
Carleer, K. Chance, C. Clerbaux, V. Dana, V. M. Devi, A. Fayt, J.-M. Flaud,
R. R. Gamache, A. Goldman, D. Jacquemart, K. W. Jucks, W. J. Lafferty, J.-Y.
Mandin, S. T. Massie, V. Nemtchinov, D. A. Newnham, A. Perrin, C. P.
Rinsland, J. Schroeder, K. M. Smith, M. A. H. Smith, K. Tang, R. A. Toth,
J. V. Auwera, P. Varanasi, and K. Yoshino, The HITRAN molecular
spectroscopic database: Edition of 2000 including updates of 2001, J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transfer, 82, 2003.
- 154
- Rothrock, D. A., and A. S. Thorndike, Measuring the sea ice floe size
distribution, J. Geophys. Res., 89, 6477-6486, 1984.
- 155
- Sangster, W. E., A meteorological coordinate system in which the Earth's
surface is a coordinate surface, Ph.D. thesis, University of Chicago,
Department of Geophysical Sciences, 1960.
- 156
- Sato, R. K., L. M. Bath, D. L. Williamson, and G. S. Williamson, User's guide
to NCAR CCMOB, Technical Report NCAR/TN-211+IA, National Center for
Atmospheric Research, Boulder, Colorado, 133 pp., 1983.
- 157
- Simmons, A. J., and D. M. Burridge, An energy and angular momentum conserving
vertical finite-difference scheme and hybrid vertical coordinates, Mon.
Wea. Rev., 109, 758-766, 1981.
- 158
- Simmons, A. J., and R. Strüfing, An energy and angular-momentum conserving
finite-difference scheme, hybrid coordinates and medium-range weather
prediction, Technical Report ECMWF Report No. 28, European Centre for
Medium-Range Weather Forecasts, Reading, U.K., 68 pp., 1981.
- 159
- Simmons, A. J., and R. Strüfing, Numerical forecasts of stratospheric
warming events using a model with hybrid vertical coordinate, Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc., 109, 81-111, 1983.
- 160
- Slingo, A., A GCM parameterization for the shortwave radiative properties of
clouds, J. Atmos. Sci., 46, 1419-1427, 1989.
- 161
- Slingo, J. M., The development and verification of a cloud prediction scheme
for the ECMWF model, Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc., 113, 899-927,
1987.
- 162
- Smith, S. J., H. Pitcher, and T. M. L. Wigley, Global and regional
anthropogenic sulfur dioxide emissions, Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles, 29, 99-119, 2001.
- 163
- Stamnes, K., S. C. Tsay, W. Wiscombe, and K. Jayaweera, A numerically stable
algorithm for discrete-ordinate-method radiative transfer in multiple
scattering and emitting layered media, Appl. Opt., 27,
2502-2509, 1988.
- 164
- Starr, V. P., A quasi-lagrangian system of hydrodynamical equations, J. Meteor., 2, 227-237, 1945.
- 165
- Steele, M., Sea ice melting and floe geometry in a simple ice-ocean model,
J. Geophys. Res., 97, 17,729-17,738, 1995.
- 166
- Stenchikov, G. L., I. Kirchner, A. Robock, H. F. Graf, J. C. Antuna, R. G.
Grainger, A. Lambert, and L. Thomason, Radiative forcing from the 1991
Mount Pinatubo volcanic eruption, J. Geophys. Res., 103,
13837-13857, 1998.
- 167
- Stowe, L. L., A. M. Ignatov, and R. R. Singh, Development, validation, and
potential enhancements to the second-generation operational aerosol product
at the National Environmental Satellite, Data, and Information
Service of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration,
J. Geophys. Res., 102, 16889-16910, 1997.
- 168
- Suarez, M. J., and L. L. Takacs, Documentation of the aries/geos dynamical
core: Version 2, Technical Report Technical Memorandum 104 606 Vol. 5, NASA,
1995.
- 169
- Sundqvist, H., Parameterization of condensation and associated clouds in models
for weather prediction and general circulation simulation, in Physically-based Modeling and Simulation of Climate and Climate Change,
Vol. 1, edited by M. E. Schlesinger, 433-461, Kluwer Academic, 1988.
- 170
- Taylor, K. E., D. Williamson, and F. Zwiers.
2001.
Amip ii sea surface temperature and sea ice concentration boundary
conditions.
http://www-pcmdi.llnl.gov/amip/AMIP2EXPDSN/BCS/amip2bcs.html 23 June
1997 (revised 6 April 2001).
- 171
- Temperton, C., Treatment of the Coriolis terms in semi-Lagrangian spectral
models, in Atmospheric and Ocean Modelling. The André J. Robert
Memorial Volume, edited by C. Lin, R. Laprise,, and H. Ritchie, 293-302,
Canadian Meteorological and Oceanographic Society, Ottawa, Canada, 1997.
- 172
- Temperton, C., M. Hortal, and A. Simmons, A two-time-level semi-Lagrangian
global spectral model, Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc., 127, 111-127,
2001.
- 173
- Tripoli, G. J., and W. R. Cotton, A numerical investigation of several factors
contributing to the observed variable intensity of deep convection over south
Florida, J. Appl. Meteorol., 19, 1037-1063, 1980.
- 174
- Troen, I., and L. Mahrt, A simple model of the atmospheric boundary layer;
sensitivity to surface evaporation, Boundary Layer Meteorol., 37,
129-148, 1986.
- 175
- Twomey, S. A., M. Piepgrass, and T. L. Wolfe, An assessment of the impact of
pollution on global cloud albedo, Tellus, 36, 356-366, 1984.
- 176
- Untersteiner, N., On the mass and heat budget of Arctic sea ice, Arch.
Meteorol. Geophys. Bioklimatol., A, 12, 151-182, 1961.
- 177
- Varanasi, P., and S. Chudamani, Infrared intensities of some
chlorofluorocarbons capable of perturbing the global climate, J. Geophys. Res., 93, 1666-1668, 1988.
- 178
- Vogelezang, D. H. P., and A. A. M. Holtslag, Evaluation and model impacts of
alternative boundary-layer height formulations, Boundary Layer
Meteorol., 81, 245-269, 1996.
- 179
- Washington, W. M., Documentation for the Community Climate Model (CCM),
Version
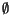 , Technical Report NTIS No. PB82 194192, National Center
for Atmospheric Research, Boulder, Colorado, 1982.
, Technical Report NTIS No. PB82 194192, National Center
for Atmospheric Research, Boulder, Colorado, 1982.
- 180
- Wesely, M. L., Parameterization of surface resistances to gaseous dry
deposition in regional-scale numerical models, Atmos. Environ., 23, 1293-1304, 1989.
- 181
- Williamson, D. L., Description of NCAR Community Climate Model
(CCM0B), Technical Report NCAR/TN-210+STR, National Center for Atmospheric
Research, Boulder, Colorado, NTIS No. PB83 23106888, 88 pp., 1983.
- 182
- Williamson, D. L., Time-split versus process-split coupling of
parameterizations and dynamical core, Mon. Wea. Rev., 130,
2024-2041, 2002.
- 183
- Williamson, D. L., L. M. Bath, R. K. Sato, T. A. Mayer, and M. L. Kuhn,
Documentation of NCAR CCM0B program modules, Technical Report
NCAR/TN-212+IA, National Center for Atmospheric Research, Boulder, Colorado,
NTIS No. PB83 263996, 198 pp., 1983.
- 184
- Williamson, D. L., J. T. Kiehl, V. Ramanathan, R. E. Dickinson, and J. J. Hack,
Description of NCAR Community Climate Model (CCM1), Technical
Report NCAR/TN-285+STR, National Center for Atmospheric Research, Boulder,
Colorado, 112 pp., 1987.
- 185
- Williamson, D. L., and J. G. Olson, Climate simulations with a
semi-Lagrangian version of the NCAR Community Climate Model, Mon. Wea. Rev., 122, 1594-1610, 1994.
- 186
- Williamson, D. L., and P. J. Rasch, Two-dimensional semi-Lagrangian transport
with shape-preserving interpolation, Mon. Wea. Rev., 117,
102-129, 1989.
- 187
- Williamson, D. L., and J. M. Rosinski, Accuracy of reduced grid calculations,
Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc., 126, 1619-1640, 2000.
- 188
- Williamson, D. L., and G. S. Williamson, Circulation statistics from January
and July simulations with the NCAR Community Climate Model
(CCM0B), Technical Report NCAR/TN-224+STR,, National Center for Atmospheric
Research, Boulder, Colorado, NTIS No. PB85 165637/AS, 112 pp., 1984.
- 189
- Williamson, G. S., CCM2 datasets and circulation statistics, Technical Report
NCAR/TN-391+STR, National Center for Atmospheric Research, Boulder, Colorado,
85 pp., 1993.
- 190
- Williamson, G. S., and D. L. Williamson, Circulation statistics from seasonal
and perpetual January and July simulations with the NCAR Community
Climate Model (CCM1): R15, Technical Report NCAR/TN-302+STR, National
Center for Atmospheric Research, Boulder, Colorado, 199 pp., 1987.
- 191
- Wiscombe, W. J., and J. W. Evans, Exponential-sum fitting of radiative
transmission functions, J. Comput. Phys., 24, 416-444, 1977.
- 192
- Xu, K.-M., and S. K. Krueger, Evaluation of cloudiness parameterizations using
a cumulus ensemble model, Mon. Wea. Rev., 119, 342-367, 1991.
- 193
- Yanai, M., S. Esbensen, and J.-H. Chu, Determination of bulk properties of
tropical cloud clusters from large-scale heat and moisture budgets, J. Atmos. Sci., 30, 611-627, 1973.
- 194
- Yin, F., D. Grosjean, and J. H. Seinfeld, Photooxidation of dimethyl sulfide
and dimethyl disulfide, I, Mechanism development, J. Atmos. Chem.,
11, 309-364, 1990a.
- 195
- Yin, F., D. Grosjean, R. C. Flagan, and J. H. Seinfeld, Photooxidation of
dimethyl sulfide and dimethyl disulfide, II, Mechanism evaluation, J. Atmos. Chem., 11, 365-399, 1990b.
- 196
- Zender, C. S., H. Bian, and D. Newman, The mineral Dust Entrainment And
Deposition (DEAD) model: Description and 1990's dust climatology, J. Geophys. Res., 108, 2003.
- 197
- Zeng, X., and R. E. Dickinson, Effect of surface sublayer on surface skin
temperature and fluxes, J. Climate, 11, 537-550, 1998.
- 198
- Zeng, X., M. Zhao, and R. E. Dickinson, Intercomparison of bulk aerodynamic
algorithms for the computation of sea surface fluxes using TOGA COARE and
TAO data, J. Climate, 11, 2628-2644, 1998.
- 199
- Zhang, G. J., and N. A. McFarlane, Sensitivity of climate simulations to the
parameterization of cumulus convection in the Canadian Climate Centre
general circulation model, Atmosphere-Ocean, 33, 407-446, 1995.
- 200
- Zhang, M., W. Lin, C. S. Bretherton, J. J. Hack, and P. J. Rasch, A modified
formulation of fractional stratiform condensation rate in the NCAR
community atmospheric model CAM2, J. Geophys. Res., 108 (D1), 2003.
- 201
- Zilitinkevich, S. S., Dynamics of the Atmospheric Boundary Layer.
Gidrometeoizdat, Leningrad, 1970, 292 pp.
Jim McCaa
2004-06-22