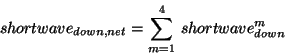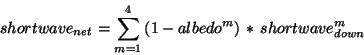Next: 6 Running the Data
Up: UsersGuide
Previous: 4 Output Datasets
Contents
Subsections
Each component model exchanges data with the coupler only. Component models have
no direct connection with each other - all data is routed through the coupler.
Most data is in the form of 2D fields. This data is accompanied by certain
timing and control information (arrays of scalar real or integer values), such
as the current simulation data and time.
All data exchanged conforms to this units convention:
Sign convention:
positive value <=> downward flux
Unit convention:
temperature ~ Kelvin
salt ~ g/kg
velocity ~ m/s
pressure ~ N/m^2 = Pa
humidity ~ kg/kg
air density ~ kg/m^3
momentum flux ~ N/m^2
heat flux ~ W/m^2
water flux ~ (kg/s)/m^2
salt flux ~ (kg/s)/m^2
coordinates ~ degrees north or east
area ~ radians^2
domain mask ~ 0 <=> an inactive grid cell
This section provides a list of the time invariant data exchanged between the
coupler and each component model. Generally this data is the "domain" data:
coordinate arrays, domain mask, cell areas, etc. It is assumed that the
domain of all models is represented by a 2D array (although not necessarily a
latitude/longitude grid).
domain data
* grid cell's center coordinates, zonal (degrees north)
* grid cell's center coordinates, meridional (degrees east)
* grid cell's four vertex coordinates, zonal (degrees north)
* grid cell's four vertex coordinates, meridional (degrees east)
* grid cell area (radians squared)
* grid cell domain mask ( 0 <=> not in active domain)
* ni,nj: the dimensions of the underlying 2D array data structure
time coordination data
* ncpl: number of times per day the component will communicate (exchange
data) with the coupler.
other information
* IC flag: indicates whether the coupler should use model IC's contained
on the coupler's restart file or IC's in the initial message sent from
the component model.
time coordination data
* date, seconds: the exact time the coupler will start the simulation from.
This section provides a list of the time-evolving data sent exchanged between
the coupler and the data model. Generally this is state, flux, and
diagnostic quantities.
Each data model provides the coupler with a set of output fields.
Output fields from a model include output states (which can be used by another
component to compute fluxes) and output fluxes (fluxes that were computed within
the model and which need to be exchanged with another component model.
The coupler provides each component model with input fields. Input fields
sent to a model include input states (the state variables of other models,
which are needed to do a flux calculation) and input fluxes (a forcing fields
computed by some other component).
Flux fields sent to or from the coupler are understood to apply over the
communication interval beginning when the data was received and ending when the
next message is received. The data models must insure that fluxes sent to
the coupler are appropriate in this context.
states
* albedo: visible , direct
* albedo: near-infrared, direct
* albedo: visible , diffuse
* albedo: near-infrared, diffuse
* surface temperature (Kelvin)
* snow height (m)
* ice fraction
* ocean fraction
* land fraction (implied by ice and ocean fractions)
fluxes
* zonal surface stress (N/m^2)
* meridional surface stress (N/m^2)
* latent heat (W/m^2)
* sensible heat (W/m^2)
* longwave radiation, upward (W/m^2)
* evaporation ((kg/s)/m^2)
diagnostic quantities
* 2 meter reference air temperature (Kelvin)
states
* layer height (m)
* zonal velocity (m/s)
* meridional velocity (m/s)
* temperature (Kelvin)
* potential temperature (Kelvin)
* pressure (Pa)
* equivalent sea level pressure (Pa)
* specific humidity (kg/kg)
* density humidity (kg/m^3)
fluxes
* precipitation: liquid, convective ((kg/s)/m^2)
* precipitation: liquid, large-scale ((kg/s)/m^2)
* precipitation: frozen, convective ((kg/s)/m^2)
* precipitation: frozen, large-scale ((kg/s)/m^2)
* longwave radiation, downward (W/m^2)
* shortwave radiation: downward, visible , direct (W/m^2)
* shortwave radiation: downward, near-infrared, direct (W/m^2)
* shortwave radiation: downward, visible , diffuse (W/m^2)
* shortwave radiation: downward, near-infrared, diffuse (W/m^2)
diagnostic quantities
* net shortwave radiation (W/m^2)
Data from the input data sequence is assumed to be daily average data. This
data is linearly interpolated in time to get instantaneous fields, and this
data is sent to the coupler. All data sent to the coupler is taken directly
from the input data sequence, with these exceptions:
- If four components of shortwave down are not present on the input data files,
they are derived from the net downward shortwave
(which must be in the input data files):
- (shortwave down, visible/direct) = 0.28 * (shortwave down, net)
- (shortwave down, visible/diffuse) = 0.24 * (shortwave down, net)
- (shortwave down, near-infrared/direct) = 0.31 * (shortwave down, net)
- (shortwave down, near-infrared/diffuse) = 0.17 * (shortwave down, net)
- Optionally (by explicitly selecting a namelist option), all shortwave fields
(net and downward) can be multiplied by an arbitrary factor.
See the flux_swfact option in the Namelist section of this document.
- If the user explicitly activates the albedo feedback option
(by default albedo feedback is not activated), the net shortwave radiation
sent to the coupler is derived using the four downward shortwave components
plus the albedos received from the coupler:
This allows the net shortwave radiation to be more consistent with the
surface albedos (e.g. sea ice extent).
See the flux_albfb option in the Namelist section of this document.
Note that this means that the latm does not ignore all input from the
coupler - latm output to the coupler is now a function of input from the
coupler.
- If sea-level pressure is missing from the input data files,
then sea-level pressure is set equal to the bottom layer pressure.
If both sea-level and bottom layer pressure is missing from the input data
files, both fields are set to 1.0e30.
- It is assumed that precipitation data on the input data files is not
divided into snow vs. rain. Where ever the bottom level atmosphere
temperature is below freezing, latm interprets precipitation to be snow.
Where ever the bottom level atmosphere temperature is above freezing,
latm interprets precipitation to be rain.




Next: 6 Running the Data
Up: UsersGuide
Previous: 4 Output Datasets
Contents
csm@ucar.edu