The File Creation Process
When just creating a replacement file for an existing one, the relevant tool should be used directly to create the file. When you are creating a set of files for a new resolution there are some dependencies between the tools that you need to keep in mind when creating them. The main dependency is that you MUST create a SCRIP grid file first as the SCRIP grid dataset is then input into the other tools. Also look at Table 3-1 which gives information on the files required and when. Figure 2-1 shows an overview of the general data-flow for creation of the fsurdat datasets.
Figure 2-1. Data Flow for Creation of Surface Datasets from Raw SCRIP Grid Files
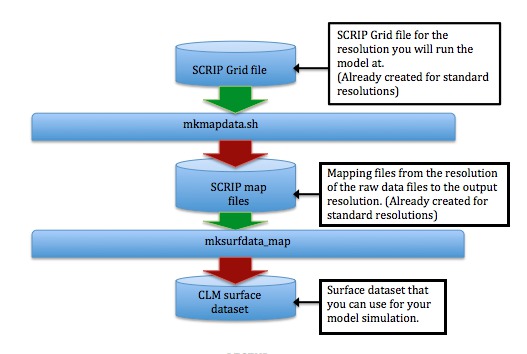
Starting from a SCRIP grid file that describes the grid you will run the model on, you first run mkmapdata.sh to create a list of mapping files. See Figure 2-3 for a more detailed view of how mkmapdata.sh works. The mapping files tell mksurfdata_map how to map between the output grid and the raw datasets that it uses as input. The output of mksurfdata_map is a surface dataset that you then use for running the model. See Figure 2-6 for a more detailed view of how mksurfdata_map works.
Figure 2-2. Legend for Data Flow Figures
Green arrows define the input to a program, while red arrows define the output. Cylinders define files that are either created by a program or used as input for a program. Boxes are programs.
Creating a Complete Set of Files for Input to CLM
Create SCRIP grid datasets (if NOT already done)
First you need to create a descriptor file for your grid, that includes the locations of cell centers and cell corners. There is also a "mask" field, but in this case the mask is set to one everywhere (i.e. all of the masks for the output model grid are "nomask"). An example SCRIP grid file is: $CSMDATA/lnd/clm2/mappingdata/grids/SCRIPgrid_10x15_nomask_c110308.nc. The mkmapgrids and mkscripgrid.ncl NCL script in the models/lnd/clm/tools/shared/mkmapgrids directory can help you with this. SCRIP grid files for all the standard CLM grids are already created for you. See the Section called Creating an output SCRIP grid file at a resolution to run the model on for more information on this.
Create domain dataset (if NOT already done)
Next use gen_domain to create a domain file for use by DATM and CLM. This is required, unless a domain file was already created. See the Section called Creating a domain file for CLM and DATM for more information on this.
Create mapping files for mksurfdata_map (if NOT already done)
Create mapping files for mksurfdata_map with mkmapdata.sh in models/lnd/clm/tools/shared/mkmapdata. See the Section called Creating mapping files that mksurfdata_map will use for more information on this.
Create surface datasets
Next use mksurfdata_map to create a surface dataset, using the mapping datasets created on the previous step as input. There is a version for either clm4_0 or clm4_5 for this program. See the Section called Using mksurfdata_map to create surface datasets from grid datasets for more information on this.
Create some sort of initial condition dataset
You then need to do one of the following three options to have an initial dataset to start from.
Use spinup-procedures to create initial condition datasets
The first option is to do the spinup procedures from arbitrary initial conditions to get good initial datasets. This is the most robust method to use. See the Section called Spinning up the Satellite Phenology Model (CLMSP spinup) in Chapter 4, the Section called Spinning up the CLM4.0 biogeochemistry Carbon-Nitrogen Model (CN spinup) in Chapter 4, or the Section called Spinning up the CLM4.0 Carbon-Nitrogen Dynamic Global Vegetation Model (CNDV spinup) in Chapter 4 for more information on this.
Use interpinic to interpolate existing initial condition datasets
The next option is to interpolate from spunup datasets at a different resolution, using interpinic. There is a version for either clm4_0 or clm4_5 for this program. See the Section called Using interpinic to interpolate initial conditions to different resolutions for more information on this.
Start up from arbitrary initial conditions
The last alternative is to run from arbitrary initial conditions without using any spun-up datasets. This is inappropriate when using CLM4.5-BGC or CLMCN (bgc=cn or cndv) as it takes a long time to spinup Carbon pools.
Warning This is NOT recommended as many fields in CLM take a long time to equilibrate.
Enter the new datasets into the build-namelist XML database
The last optional thing to do is to enter the new datasets into the build-namelist XML database. See Chapter 3 for more information on doing this. This is optional because the user may enter these files into their namelists manually. The advantage of entering them into the database is so that they automatically come up when you create new cases.
The models/lnd/clm/tools/README goes through the complete process for creating input files needed to run CLM. We repeat that file here:
models/lnd/clm/tools/README Jun/04/2013
CLM tools for analysis of CLM history files -- or for creation or
modification of CLM input files.
I. General directory structure:
clm4_0
mksurfdata_map --- Create surface datasets.
interpinic ------- Interpolate initial datasets to a different resolution.
(has optimized and OMP options)
clm4_5
mksurfdata_map --- Create surface datasets.
interpinic ------- Interpolate initial datasets to a different resolution.
(has optimized and OMP options)
shared
mkmapgrids ------- Create SCRIP grid files needed by mkmapdata
[input is CLM grid files]
(deprecated)
mkmapdata -------- Create SCRIP mapping data from SCRIP grid files (uses ESMF)
gen_domain ------- Create data model domain datasets from SCRIP mapping datasets.
(also in the top level mapping directory [../../../../tools/mapping])
mkprocdata_map --- Convert output unstructured grids into a 2D format that
can be plotted easily
ncl_scripts ------ NCL post or pre processing scripts.
Note that there are different versions of mksurfdata_map and interpinic for
CLM4.0 vs. CLM4.5. Other tools are shared between the two model
versions.
However, note that mkmapdata makes mapping files for CLM4.5 by default; to
make mapping files for CLM4.0, run the tool with the option:
-p clm4_0
II. Notes on building/running for each of the above tools:
Each tool that has FORTRAN source code has the following files:
README -------------- Specific help for using the specific tool and help on specific
files in that directory.
src/Filepath -------- List of directories needed to build the tool
(some files in ../src directories are required).
src/Makefile -------- Customization of the make for the particular tool in question
src/Makefile.common - General GNU Makefile for creating FORTRAN tools
(these are identical between tools).
src/Srcfiles -------- List of source files that are needed.
src/Mkdepends ------- Dependency generator program
mkmapdata and ncl_scripts only contain scripts so don't have the above build files.
Most tools have copies of files from other directories -- see the README.filecopies
file for more information on this.
Tools may also have files with the directory name followed by: namelist, or runoptions.
<directory>.namelist ------ Namelist to create a global file.
<directory>.runoptions ---- Command line options to use the given tool.
These files are also used by the test scripts to test the tools (see the
README.testing) file.
NOTE: Be sure to change the path of the datasets references by these namelists to
point to where you have exported your CESM inputdata datasets.
To build:
cd <directory>
setenv INC_NETCDF <path-to-NetCDF-include-files>
setenv LIB_NETCDF <path-to-NetCDF-library-files>
gmake
The process will create a file called "Depends" which has the dependencies
for the build of each file on other files.
By default some codes may be compiled non-optimized
so that you can use the debugger, and with bounds-checking, and float trapping on.
To speed up do the following...
gmake OPT=TRUE (by default already on for interpinic and mksurfdata_map)
Also some of the tools allow for OpenMP shared memory parallelism
(such as interpinic) with
gmake SMP=TRUE
To run a program with a namelist:
./program < namelist
To get help on running a program with command line options (e.g., interpinic):
./program
To run a program built with SMP=TRUE:
setenv OMP_NUM_THREADS=<number_of_threads_to_use>
run normally as above
III. Process sequence to create input datasets needed to run CLM
NOTE: The following assumes you want to create files for CLM4.5. If you want to
use CLM4.0, you will need to do the following:
- In the following commands, change references to the clm4_5 directory to clm4_0
- Add the option '-p clm4_0' to the mkmapdata.sh command.
1.) Create SCRIP grid files (if needed)
a.) For standard resolutions these files will already be created. (done)
b.) To create regular lat-lon regional/single-point grids run mknoocnmap.pl
This will create both SCRIP grid files and a mapping file that will
be valid if the region includes NO ocean whatsoever (so you can skip step 2).
You can also use this script to create SCRIP grid files for a region
(or even a global grid) that DOES include ocean if you use step 2 to
create mapping files for it (simply discard the non-ocean map created by
this script).
Example, for single-point over Boulder Colorado.
cd shared/mkmapdata
./mknoocnmap.pl -p 40,255 -n 1x1_boulderCO
c.) General case
You'll need to convert or create SCRIP grid files on your own (using scripts
or other tools) for the general case where you have an unstructured grid, or
a grid that is not regular in latitude and longitude.
example format
==================
netcdf fv1.9x2.5_090205 {
dimensions:
grid_size = 13824 ;
grid_corners = 4 ;
grid_rank = 2 ;
variables:
double grid_center_lat(grid_size) ;
grid_center_lat:units = "degrees" ;
double grid_center_lon(grid_size) ;
grid_center_lon:units = "degrees" ;
double grid_corner_lat(grid_size, grid_corners) ;
grid_corner_lat:units = "degrees" ;
double grid_corner_lon(grid_size, grid_corners) ;
grid_corner_lon:units = "degrees" ;
int grid_dims(grid_rank) ;
int grid_imask(grid_size) ;
grid_imask:units = "unitless" ;
2.) Create ocean to atmosphere mapping file (if needed)
a.) Standard resolutions (done)
If this is a standard resolution with a standard ocean resolution -- this
step is already done, the files already exist.
b.) Region without Ocean (done in step 1.b)
IF YOU RAN mknoocnmap.pl FOR A REGION WITHOUT OCEAN THIS STEP IS ALREADY DONE.
c.) New atmosphere or ocean resolution
If the region DOES include ocean, use gen_domain to create a
mapping file for it.
Example:
cd ../../../../tools/mapping/gen_domain_files/src
./gen_domain -m $MAPFILE -o $OCNGRIDNAME -l $ATMGRIDNAME
3.) Add SCRIP grid file(s) created in (1) into XML database in CLM (optional)
See the "Adding New Resolutions or New Files to the build-namelist Database"
Chapter in the CLM User's Guide
http://www.cesm.ucar.edu/models/cesm1.0/clm/models/lnd/clm/doc/UsersGuide/book1.html
If you don't do this step, you'll need to specify the file to mkmapdata
in step (3) using the "-f" option.
4.) Create mapping files for use by mksurfdata_map with mkmapdata
(See mkmapdata/README for more help on doing this)
- this step uses the results of (1) that were entered into the XML database
by step (3). If you don't enter datasets in, you need to specify the
SCRIP grid file using the "-f" option to mkmapdata.sh.
- note that mkmapdata generates maps for CLM4.5 by default; to generate
mapping files for CLM4.0, add the option '-p clm4_0'
Example: to generate all necessary mapping files for the ne30np4 grid
cd shared/mkmapdata
./mkmapdata.sh -r ne30np4
5.) Add mapping file(s) created in step (4) into XML database in CLM (optional)
See notes on doing this in step (3) above.
Edit ../bld/namelist_files/namelist_defaults_clm.xml to incorporate new
mapping files.
If you don't do this step, you'll need to specify the grid resolution name
and file creation dates to mksurfdata_map in step (5) below.
6.) Convert map of ocean to atm for use by DATM and CLM with gen_domain
(See tools/mapping/README for more help on doing this)
- gen_domain uses the map from step (2) (or previously created CESM maps)
Example:
cd ../../../../tools/mapping/gen_domain_files/src
gmake
cd ..
setenv CDATE 090206
setenv OCNGRIDNAME gx1v6
setenv ATMGRIDNAME fv1.9x2.5
setenv MAPFILE $CSMDATA/cpl/cpl6/map_${OCNGRIDNAME}_to_${ATMGRIDNAME}_aave_da_${CDATE}.nc
./gen_domain -m $MAPFILE -o $OCNGRIDNAME -l $ATMGRIDNAME
Normally for I compsets running CLM only you will discard the ocean domain
file, and only use the atmosphere domain file for datm and as the fatmlndfrc
file for CLM. Output domain files will be named according to the input OCN/LND
gridnames.
7.) Create surface datasets with mksurfdata_map
(See mksurfdata_map/README for more help on doing this)
- Run clm4_5/mksurfdata_map/mksurfdata.pl
- This step uses the results of step (4) entered into the XML database
in step (5).
- If datasets were NOT entered into the XML database, set the resolution
to "usrspec" and use the "-usr_gname", and "-usr_gdate" options.
Example: for 0.9x1.25 resolution
cd clm4_5/mksurfdata_map/src
gmake
cd ..
./mksurfdata.pl -r 0.9x1.25
NOTE that surface dataset will be used by default for fatmgrid - and it will
contain the lat,lon,edges and area values for the atm grid - ASSUMING that
the atm and land grid are the same
8.) Interpolate initial conditions using interpinic (optional)
(See interpinic/README for more help on doing this)
IMPORTANT NOTE on interpinic!!!:: BE SURE TO USE NetCDF4.3 WHEN BUILDING!
If your template file was written using pnetcdf -- interpinic will corrupt
the resulting file and make it unusable!
9.) Add new files to XML data or using user_nl_clm (optional)
See notes on doing this in step (3) above.
IV. Example of creating single-point datasets without entering into XML database.
Here we apply the process described in III. for a single-point dataset
where we don't enter the datasets into the XML database (thus skipping
steps 3, 5 and 9), but use the needed command line options to specify where the
files are. This also skips step (2) since step 1 creates the needed mapping file.
We also skip step (8) and do NOT create a finidat file.
0.) Set name of grid to use and the creation date to be used later...
setenv GRIDNAME 1x1_boulderCO
setenv CDATE `date +%y%m%d`
1.) SCRIP grid and atm to ocn mapping file
cd shared/mkmapdata
./mknoocnmap.pl -p 40,255 -n $GRIDNAME
# Set pointer to MAPFILE that will be used in step (6)
setenv MAPFILE `pwd`/map_${GRIDNAME}_noocean_to_${GRIDNAME}_nomask_aave_da_${CDATE}.nc
cd ../..
2.) skip
3.) skip
4.) Mapping files needed for mksurfdata_map
cd shared/mkmapdata
setenv GRIDFILE ../mkmapgrids/SCRIPgrid_${GRIDNAME}_nomask_${CDATE}.nc
./mkmapdata.sh -r $GRIDNAME -f $GRIDFILE -t regional
cd ..
5.) skip
6.) Generate domain file for datm and CLM
cd ../../../../tools/mapping/gen_domain_files/src
gmake
cd ..
setenv OCNDOM domain.ocn_noocean.nc
setenv ATMDOM domain.lnd.{$GRIDNAME}_noocean.nc
./gen_domain -m $MAPFILE -o $OCNDOM -l $ATMDOM
cd ../../../../lnd/clm/tools
7.) Create surface dataset for CLM
cd clm4_5/mksurfdata_map/src
gmake
cd ..
./mksurfdata.pl -r usrspec -usr_gname $GRIDNAME -usr_gdate $CDATE
8.) skip
9.) skip
V. Notes on which input datasets are needed for CLM
global or regional/single-point grids
- need fsurdata and fatmlndfrc
fsurdata ---- from mksurfdata_map in step (III.7)
fatmlndfrc -- use the domain.lnd file from gen_domain in step (III.6)
(NOTE: THIS FILE IS POINTED TO USING ATM_DOMAIN_PATH/ATM_DOMAIN_FILE/LND_DOMAIN_PATH/ \
LND_DOMAIN_FILE
env_run.xml variables -- do NOT simply add this to your user_nl_clm as it will fail)
|