- 3.1.1 Generalized terrain-following vertical coordinates
- 3.1.2 Conversion to final form
- 3.1.3 Continuous equations using
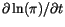
- 3.1.4 Semi-implicit formulation
- 3.1.5 Energy conservation
- 3.1.6 Horizontal diffusion
- 3.1.7 Finite difference equations
- 3.1.8 Time filter
- 3.1.9 Spectral transform
- 3.1.10 Spectral algorithm overview
- 3.1.11 Combination of terms
- 3.1.12 Transformation to spectral space
- 3.1.13 Solution of semi-implicit equations
- 3.1.14 Horizontal diffusion
- 3.1.15 Initial divergence damping
- 3.1.16 Transformation from spectral to physical space
- 3.1.17 Horizontal diffusion correction
- 3.1.18 Semi-Lagrangian Tracer Transport
- 3.1.19 Mass fixers
- 3.1.20 Energy Fixer
- 3.1.21 Statistics Calculations
- 3.1.22 Reduced grid
- 3.2.1 Introduction
- 3.2.2 Vertical coordinate and hydrostatic equation
- 3.2.3 Semi-implicit reference state
- 3.2.4 Perturbation surface pressure prognostic variable
- 3.2.5 Extrapolated variables
- 3.2.6 Interpolants
- 3.2.7 Continuity Equation
- 3.2.8 Thermodynamic Equation
- 3.2.9 Momentum equations
- 3.2.10 Development of semi-implicit system equations
- 3.2.11 Trajectory Calculation
- 3.2.12 Mass and energy fixers and statistics calculations
- 3.3.1 Overview
- 3.3.2 The governing equations for the hydrostatic atmosphere
- 3.3.3 Horizontal discretization of the transport process on the sphere
- 3.3.4 A vertically Lagrangian and horizontally Eulerian control-volume discretization of the hydrodynamics
- 3.3.5 A mass, momentum, and total energy conserving mapping algorithm
- 3.3.6 Adjustment of specific humidity to conserve water
- 3.3.7 Further discussion